Guide to Alien Landholding License Laws in Saint Lucia
Introduction
Saint Lucia, a gem in the Eastern Caribbean, is a prime destination for international investors seeking opportunities in paradise. The island’s real estate market, from luxurious beachfront villas to verdant inland estates, offers significant appeal. However, for non-citizens, acquiring property in Saint Lucia requires compliance with the Alien Landholding License (ALHL) laws—a crucial regulatory framework designed to balance national interests with foreign investment.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and navigating the ALHL system, covering its purpose, requirements, and practical tips for success.
What is the Alien Landholding License?
The Alien Landholding License (ALHL) is a legal requirement for non-citizens purchasing or leasing property in Saint Lucia for more than three years. It applies across all property types—residential, commercial, and agricultural—and ensures that foreign investments align with the nation’s developmental and environmental goals.
Quick Facts About the ALHL:
- Purpose: Regulates foreign land ownership to protect national interests.
- Applies to: Individuals, companies, and trusts involving non-citizens.
- Introduced: Strengthened under the Alien Landholding (Licensing) Act No. 1 of 2020.
Purpose of the ALHL Laws
The ALHL system serves as more than just a bureaucratic hurdle; it plays a vital role in safeguarding Saint Lucia’s economic and social landscape.
| Key Objectives | Description |
|---|---|
| Protect Local Land | Limits foreign ownership to prevent overconcentration of land in non-citizen hands. |
| Encourage Investment | Promotes projects that boost the economy, such as eco-tourism and commercial ventures. |
| Preserve the Environment | Ensures sustainable development and conservation of Saint Lucia’s pristine ecosystems. |
| Revenue Generation | Licensing fees and taxes contribute to national infrastructure and community programs. |
Who Needs an Alien Landholding License?
The ALHL applies to all non-citizens looking to acquire property or lease land for extended periods.
Examples of Transactions Requiring an ALHL:
- Purchasing a residential villa for personal use.
- Leasing agricultural land for more than three years.
- Acquiring shares in a company that owns real estate.
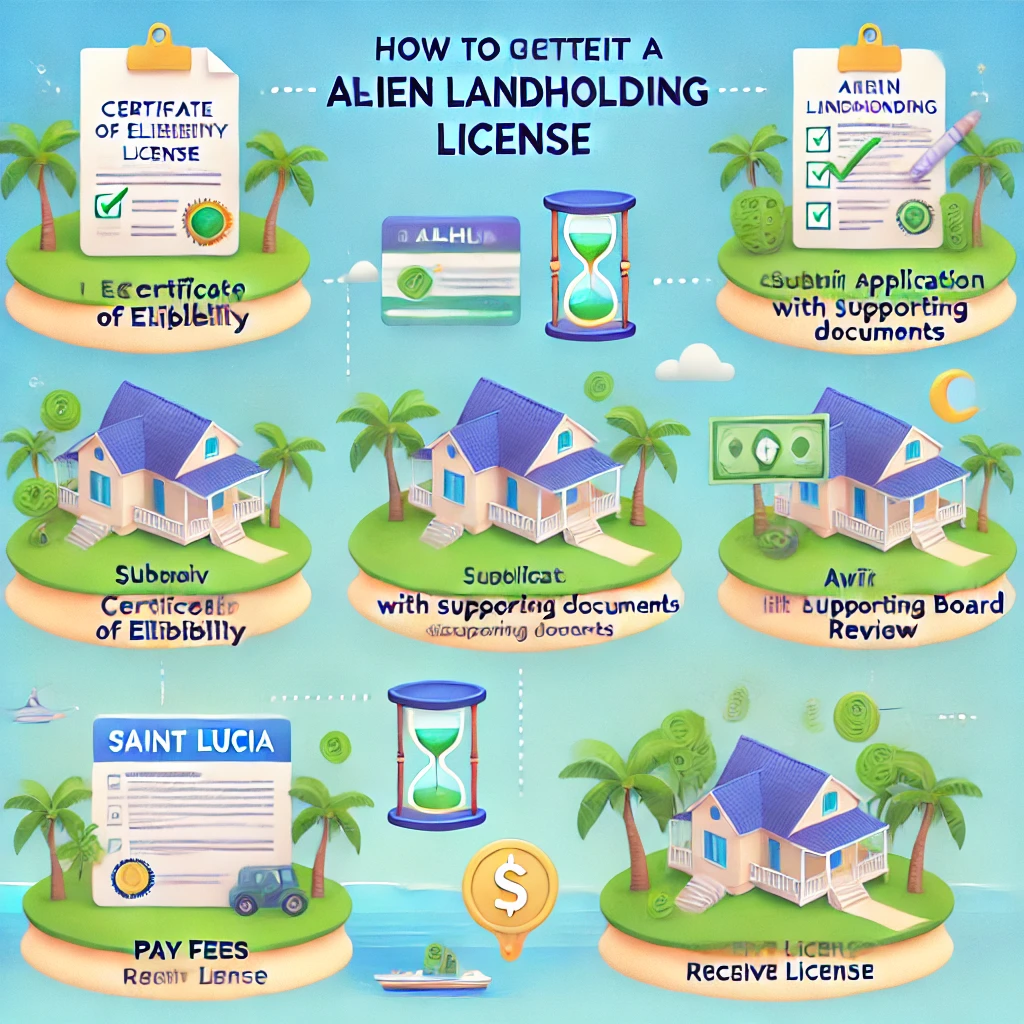
The Application Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Acquiring an ALHL involves multiple steps and careful preparation.
Step 1: Certificate of Eligibility
This certificate proves you meet the preliminary requirements to hold land in Saint Lucia.
- Required Documents:
- Valid passport and identification.
- Police clearance certificates.
- Proof of financial capability (bank statements or letters).
Step 2: Application Submission
After obtaining the Certificate of Eligibility, the ALHL application is submitted to the Alien Landholding Licensing Board.
- Documents Needed:
- Detailed property description and intended use.
- Certified copies of corporate documents (if applying as a company).
Step 3: Licensing Board Review
The Board evaluates the application, consulting with government agencies to ensure compliance with national interests.
Step 4: License Issuance
Once approved, the license is granted with specific conditions, such as a development timeline or resale restrictions.
Associated Costs
Understanding the financial aspects of acquiring an ALHL is critical for successful planning.
| Type of Fee | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Certificate of Eligibility | Varies based on one-year or ten-year validity terms. |
| License Application Fee | Determined by property value and intended use. |
| Legal Fees | Ranges from 3-5% of property value for attorneys. |
| Stamp Duty & Transfer Tax | Typically 2% to 5% of the purchase price. |
Conditions and Restrictions
License holders must adhere to specific conditions that regulate how the property is used and managed.
- Development Deadlines
- Undeveloped land may require construction within a set timeframe.
- Resale Approval
- Government consent may be required before selling the property to another party.
- Environmental Compliance
- Projects must meet regulations protecting natural resources, particularly in eco-sensitive areas.
Benefits of the ALHL for Investors
Investors who comply with ALHL laws gain several advantages, including:
1. Secure Land Ownership
- The ALHL ensures clear and enforceable property rights under Saint Lucian law.
2. Access to High-Value Real Estate
- From beachfront homes to agricultural estates, the ALHL opens doors to prime properties.
3. Enhanced Investment Opportunities
- Owning land enables investors to participate in lucrative sectors such as tourism and hospitality.
4. Pathway to Residency
- Property ownership can strengthen applications for residency or citizenship via the Citizenship by Investment Program (CIP).
Challenges of the ALHL System
Despite its benefits, the ALHL process has some limitations:
- Lengthy Processing Times: Applications can take several months due to thorough vetting.
- High Costs: Fees and legal expenses may deter smaller investors.
- Complex Regulations: Compliance requires significant legal and financial expertise.
Case Studies: Successful ALHL Projects
Case 1: Boutique Resort Development
A European investor obtained an ALHL to establish a luxury eco-resort near Soufrière. The project has contributed to local employment and sustainable tourism while preserving the natural landscape.
Case 2: Residential Villas in Rodney Bay
An American family used the ALHL system to acquire land and build a private villa. Their success highlights the transparency of the application process when managed by local professionals.
Expert Tips for Navigating the ALHL Process
1. Partner with Local Professionals
Hire a local attorney experienced in real estate law to handle your application.
2. Plan for Hidden Costs
Account for taxes, attorney fees, and compliance expenses in your budget.
3. Conduct Thorough Due Diligence
Before purchasing, verify the property’s title, zoning restrictions, and development history.
4. Understand ALHL Conditions
Familiarize yourself with any development or resale restrictions tied to your license.
5. Think Long-Term
Invest in properties that align with Saint Lucia’s growth sectors, such as tourism or agriculture.
Visual Elements
Infographic: Steps to Obtain the ALHL
- Obtain Certificate of Eligibility.
- Submit Application with Supporting Documents.
- Await Board Review.
- Pay Fees and Receive License.
Chart: Cost Breakdown of ALHL Transactions
| Expense Type | % of Property Value |
|---|---|
| Application Fees | 2-3% |
| Legal and Professional Fees | 3-5% |
| Stamp Duty | 2% |
Photo Idea: Prime Real Estate in Saint Lucia
Include images of:
- Beachfront villas in Rodney Bay.
- Luxury resorts in Soufrière.
- Undeveloped land ripe for agricultural projects.
The Alien Landholding License laws in Saint Lucia create a balanced framework that welcomes foreign investment while safeguarding the island’s resources and interests. Though the application process requires careful preparation and financial planning, the rewards are significant for those looking to invest in one of the Caribbean’s most beautiful and dynamic nations.
Whether your goal is a serene retirement villa, a commercial venture in tourism, or an agricultural project, the ALHL offers a structured pathway to owning property in Saint Lucia. With the right guidance, you can turn your Caribbean dream into reality.